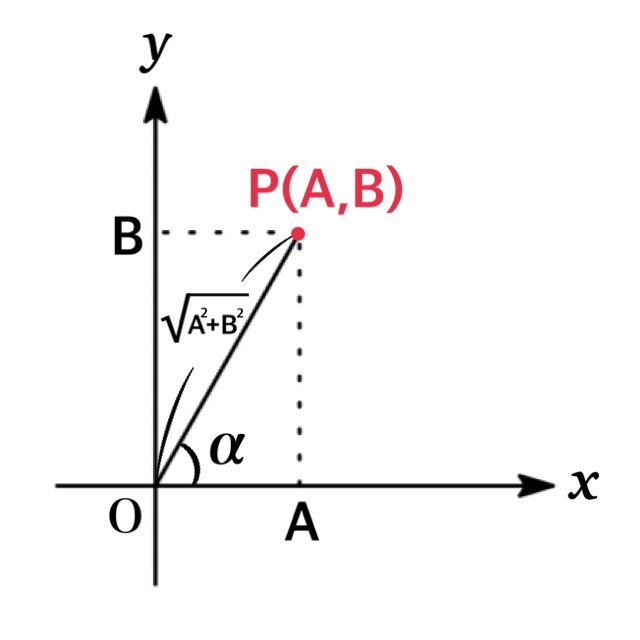
$A, \ B$ を定数とするとき, $A\sin \theta+B\cos \theta$ は次のように変形できる:
$$A\sin \theta+B\cos \theta=\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\sin (\theta +\alpha)$$
ただし $\cos \alpha=\frac{A}{\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}}, \ \sin \alpha=\frac{B}{\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}}$
与えられた $A,\ B$ に対して, $xy$ 平面上に点 $P(A, B)$ をとると
$$OP=\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}$$
で表される. また $OP$ と $x$ 軸の正部分 がなす角を $\alpha$ とすれば
$$A=\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cdot \cos\alpha,\ \ \ B=\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cdot \sin\alpha$$
よって
\begin{eqnarray*}A\sin \theta+B\cos \theta&=&\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cdot \cos\alpha\sin\theta+\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cdot \sin\alpha\cos\theta\\&=&\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}(\sin\theta\cos\alpha+\cos\theta\sin\alpha)\\&=&\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\sin (\theta +\alpha)\end{eqnarray*}
NOTE:$A,\ B$ を定数とするとき, $\theta$ の関数 $y=A\sin\theta+B\cos\theta$ は $y=\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\sin (\theta +\alpha)$ と変形できるので, その最大値は $\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}$ , 最小値は $-\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}$ となる.
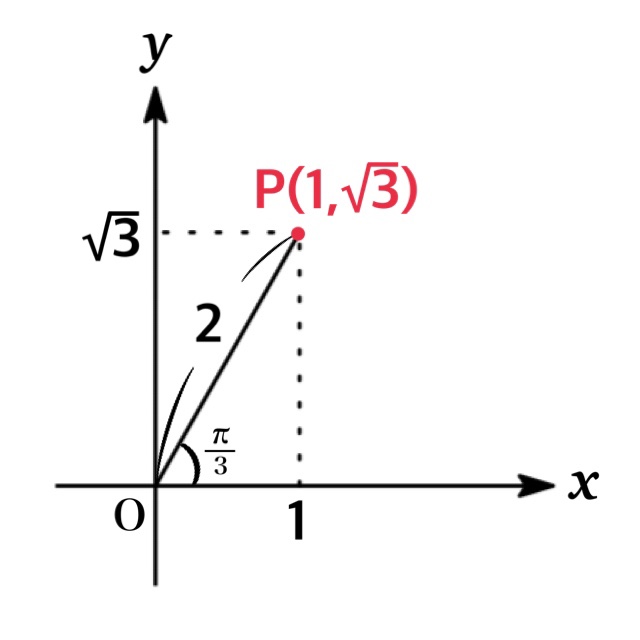
例題
$\sin\theta+\sqrt{3}\cos\theta$ を $r\sin(\theta+\alpha)$ の形に変形してみよう.
$A = (\sin\theta$ の係数 $)=1$, $B=(\cos\theta$ の係数 $)=\sqrt{3}$ より
$$\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}=\sqrt{1^{2}+(\sqrt{3})^{2}}=2$$
また $P(1,\ \sqrt{3})$ に対して $OP$ と$x$ 軸の正部分がなす角は $\alpha=\frac{\pi}{3}$ より
$$y=\sin\theta+\sqrt{3}\cos\theta=2\sin(\theta+\frac{\pi}{3})$$
と変形できる.
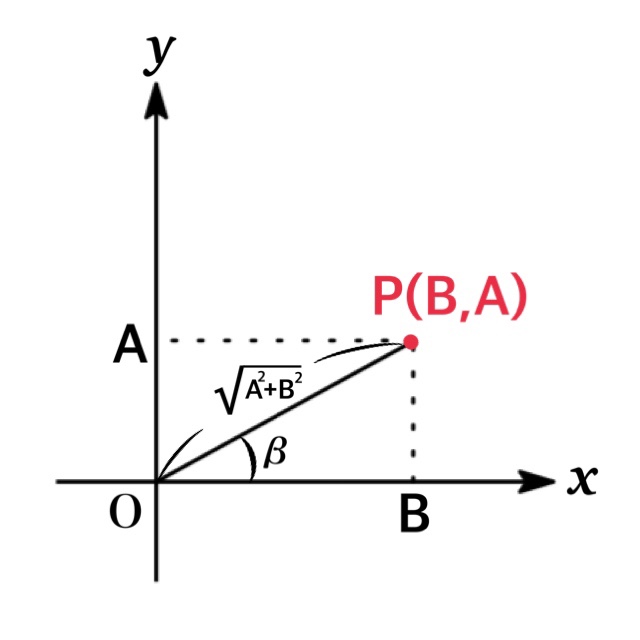
注意
三角関数の合成は $\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cos (\theta -\beta)$ の形に変形することもできる.
$A, \ B$ を定数とするとき
$$A\sin\theta +B\cos \theta=\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cos (\theta -\beta)$$
ただし $\sin \beta=\frac{A}{\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}}, \ \cos \beta=\frac{B}{\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}}$
この場合, $A,\ B$ に対して, $xy$ 平面上に点 $P(B, A)$をとり, $OP$ と $x$ 軸の正部分 がなす角を $\beta$ とすれば
$$A=\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cdot \sin\beta,\ \ \ B=\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cdot \cos\beta$$
\begin{eqnarray*}A\sin \theta+B\cos \theta&=&\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cdot \sin\beta\sin\theta+\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cdot \cos\beta\cos\theta\\&=&\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}(\sin\theta\sin\beta+\cos\theta\cos\beta)\\&=&\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}\cos (\theta -\beta)\end{eqnarray*}
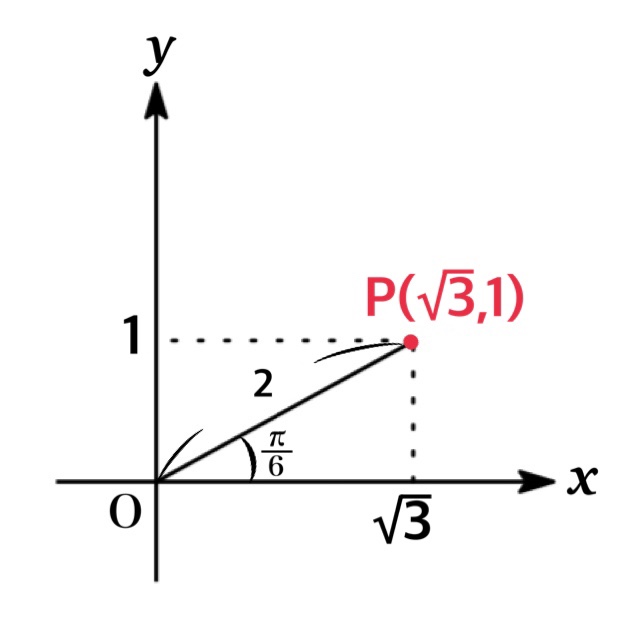
例題
$\sin\theta+\sqrt{3}\cos\theta$ を $r\cos(\theta-\beta)$ の形に変形してみよう.
$A = (\sin\theta$ の係数 $)=1$, $B=(\cos\theta$ の係数 $)=\sqrt{3}$ より
$$\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}=\sqrt{1^{2}+(\sqrt{3})^{2}}=2$$
また $P(\sqrt{3},\ 1)$ に対して $OP$ と$x$ 軸の正部分がなす角は $\beta=\frac{\pi}{6}$ より
$$y=\sin\theta+\sqrt{3}\cos\theta=2\cos(\theta-\frac{\pi}{6})$$
と変形できる.